|
|
1.day15
1.1异常
1.1.1错误和异常
Error 错误 是代表JVM本身的错误, 咱们程序员无法通过代码进行处理的
Exception 异常 代表Java程序在运行过程中出现了不可预期的错,然后影响了代码的正常的执行,可以使用Java中的异常的处理机制抛出来一下代码,让代码能够正常的执行下去。
Java 8 中文版 - 在线API中文手册 - 码工具 (matools.com)
1.1.2Throwable【开发不用】
Java是面向对象开发的,Java中封装好了一个类叫Throwable类,这个类是专门处理错误和异常的类。
学会官方的API手册:
1.先看这个类是否是接口 类 或者抽象类
2.要看继承关系
3.构造方法(目的是啥? 是否能实例化)
4.看方法
构造方法:
Throwable()构造一个新的可抛出的 null作为其详细信息。
Throwable(String message)构造一个具有指定的详细消息的新的throwable。
方法:
| String | getMessage()返回此throwable的详细消息字符串。 | | void | printStackTrace()将此throwable和其追溯打印到标准错误流。 |
package com.qf.c_throwable;
public class Demo1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Throwable throwable = new Throwable();
System.out.println(throwable);//java.lang.Throwable
//构造一个新的可抛出的 null作为其详细信息的一个对象
System.out.println(throwable.getMessage());//null
//Throwable(String message)
//构造一个具有指定的详细消息的新的throwable。
Throwable throwable2 = new Throwable("狗蛋");
System.out.println(throwable2.getMessage());//标准的输出流
throwable2.printStackTrace();//没有返回值 是不能sout的
//标准错误流是在控制台显示红色的
/**
* java.lang.Throwable: 狗蛋
at com.qf.c_throwable.Demo1.main(Demo1.java:13)
*/
System.out.println("qwer");
}
}
1.1.3异常【重点】
1.1.3.1异常的捕捉
语法格式
try{//尝试
可能出现异常的代码
}catch(异常对象){
异常的处理方法
}
如果try后面大括号里的代码无异常就会跳过catch,继续执行下面的代码
如果try后面大括号里的代码有异常就会执行catch内的异常处理方法,后面的代码继续执行
package com.qf.d_exception;
public class Demo1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
test(3, 0);
}
public static void test(int a, int b) {
// Exception in thread "main" java.lang.ArithmeticException: / by zero
// at com.qf.d_exception.Demo1.test(Demo1.java:8)
// at com.qf.d_exception.Demo1.main(Demo1.java:5)
int c = 0;
try {
c = a / b;
}catch (Exception e) {//catch 抓 捕捉
//Exception e = new ArithmeticException(); 多态
//jvm会抛出一个异常的实例(对象) 将对象赋值给ArithmeticException e = new ArithmeticException()
System.out.println("代码有异常,你自己看着办");
System.out.println("除数不能为0");
}
System.out.println(c);
System.out.println("嘻嘻");
}
}语法格式
多个异常
try{
可能出现异常的代码
}catch(异常对象1){
异常的处理方法
}catch(异常对象2){
异常的处理方法
}或
try{
可能出现异常的代码
}catch(异常对象1 | 异常对象2 ){
异常的处理方法
}
package com.qf.d_exception;
public class Demo2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] arr = new int[2];
test(3, 1, arr);
}
public static void test(int a, int b, int[] arr) {
int c = 0;
try {
c = a / b;//除数为0 jvm抛出一个异常ArithmeticException
arr[4] = 20;//jvm抛出一个异常ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException
} catch (ArithmeticException e) {
System.out.println("除数不能为0");
} catch (ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException e) {
System.out.println("数组下标越了界");
}
System.out.println("代码结束了");
}
}
package com.qf.d_exception;
public class Demo3 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] arr = new int[2];
test(3, 0, arr);
}
public static void test (int a, int b, int[] arr) {
int c = 0;
try {
c = a / b;//除数为0 jvm抛出一个异常ArithmeticException
arr[4] = 20;//jvm抛出一个异常ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException
} catch (ArithmeticException | ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException e) {
System.out.println("除数不能为0或者数组下标越界");
}
System.out.println("代码结束了");
}
}
语法格式
try {//尝试
可能出现异常代码
} catch(异常对象) {//抓
//针对于上面异常的处理方案
} finally {
最终执行的代码
}
执行流程: 如果try里面的代码没有异常,跳过catch 然后接着往下执行。
如果trye里面有异常,就执行catch后面大括号的代码
finally代码无论有没有异常都要执行
package com.qf.d_exception;
public class Demo3 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] arr = new int[2];
test(3, 1, arr);
}
public static void test (int a, int b, int[] arr) {
int c = 0;
try {
c = a / b;//除数为0 jvm抛出一个异常ArithmeticException
arr[1] = 20;//jvm抛出一个异常ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException
} catch (ArithmeticException | ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException e) {
System.out.println("除数不能为0或者数组下标越界");
}finally {
//最终的 无论有没有异常都要执行的
System.out.println("代码结束了");
}
}
}
package com.qf.d_exception;
public class Demo4 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] arr = new int[2];
test(3, 0, arr);
}
public static void test (int a, int b, int[] arr) {
int c = 0;
try {
c = a / b;//除数为0 jvm抛出一个异常ArithmeticException
arr[4] = 20;//jvm抛出一个异常ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException
} catch (Exception e) {
System.out.println("除数不能为0或者数组下标越界");
System.out.println(e.getMessage());/// by zero
}
System.out.println("代码结束了");
}
}
1.1.3.2异常的抛出
throws 名词 抛 语法格式:throws 异常类 提醒此处有异常,书写小心
package com.qf.d_exception;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.FileNotFoundException;
public class Demo5 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception{
//在当前出现异常代码所在的方法的后面 书写关键字 throws 异常类
Thread.sleep(1000);
FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream(new File("c:/aaa/1.txt"));
}
}
总结: 在有异常的地方的方法的后面 throws 异常类
1.1.3.3throw
throw 动词 抛出 语法格式:throw 异常对象
package com.qf.d_exception;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Demo6 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception{
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("请输入用户名:");
String username = scanner.next();
if (!username.equals( "狗蛋")) {
//throw 是抛的动作 后面跟的是一个异常的对象
//new Exception("用户名不存在"); 编译时异常
throw new Exception("用户名不存在");//造错!!!
}
System.out.println("请输入密码:");
String password = scanner.next();
if (!password.equals("123")) {
throw new Exception("密码错误");
}
System.out.println("登陆成功!!!");
}
}
throw 和throws 区别 面试
throw 是动词,抛出一个异常
throws 是名词,抛出,提醒程序员此处有异常,注意别写错
1.1.3.4自定义异常
package com.qf.d_exception;
//抄别人的异常类 单身人士的异常类
class SinglerException extends Exception{
public SinglerException () {
super();
}
public SinglerException (String message) {
super(message);
}
}
public class Demo7 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
buy(false);
}
//true 是单身 false 不是单身
public static void buy (boolean isSingle) throws Exception{
if (isSingle) {
throw new SinglerException("单身不能进店购买");
}
System.out.println("情侣买一送一!!!");
}
}
2.day16
2.1String
2.1.1String的两种声明方式
package com.qf.a_string;
public class Demo1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//声明的第一种方式:
String string = "我欲乘风归去";
System.out.println(string);
//这第二种声明方式
String str1 = new String("goudan");
System.out.println(str1);
}
}
2.1.2两个字符串比较
== 比较的是内存地址
equals 先比较内存地址,地址不一样再比较内容
package com.qf.a_string;
public class Demo2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String str1 = "abc";
String str2 = "abc";
String str3 = new String("abc");
String str4 = new String("abc");
//== 比较的是内存的地址
System.out.println(str1 == str2);//true
System.out.println(str1 == str3);//false
System.out.println(str3 == str4);//false
// boolean equals(Object anOnject); 比较两个字符串是否相等
//equals 先比较的是内存地址,如果内存地址一样 肯定是一样的。如果地址不一样 再比较内容
//内容一样的话,也true
System.out.println(str1.equals(str2));//true
System.out.println(str1.equals(str3));//true
System.out.println(str3.equals(str4));//true
/**
* "abc" a "abc"b
* a == b 内存不一样 false
* 继续比较内容
* a = {'a', 'b', 'c'} b = {'a', 'b', 'c'};
* for () {
* if (a == b) {
* a[0] == b[0]
* a[1] ==b[1]
* a[2] == b[2]
* }
*
* }
* public boolean equals(Object anObject) {
if (this == anObject) {//比较两个内存地址是否一样
return true;//内存地址一样的话就返回true
}
if (anObject instanceof String) {//true
String anotherString = (String)anObject; 强转为字符串
v1 = {'a', 'b', 'c'} v2 = {'a', 'b', 'c'};
int n = value.length;
if (n == anotherString.value.length) {
char v1[] = value;
char v2[] = anotherString.value;
int i = 0;
while (n-- != 0) {
if (v1 != v2) {
v1[0] !=v2[0]
v1[1] !=v2[1]
v1[2] !=v2[2]
return false;
}
i++;
}
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
*
*/
}
}
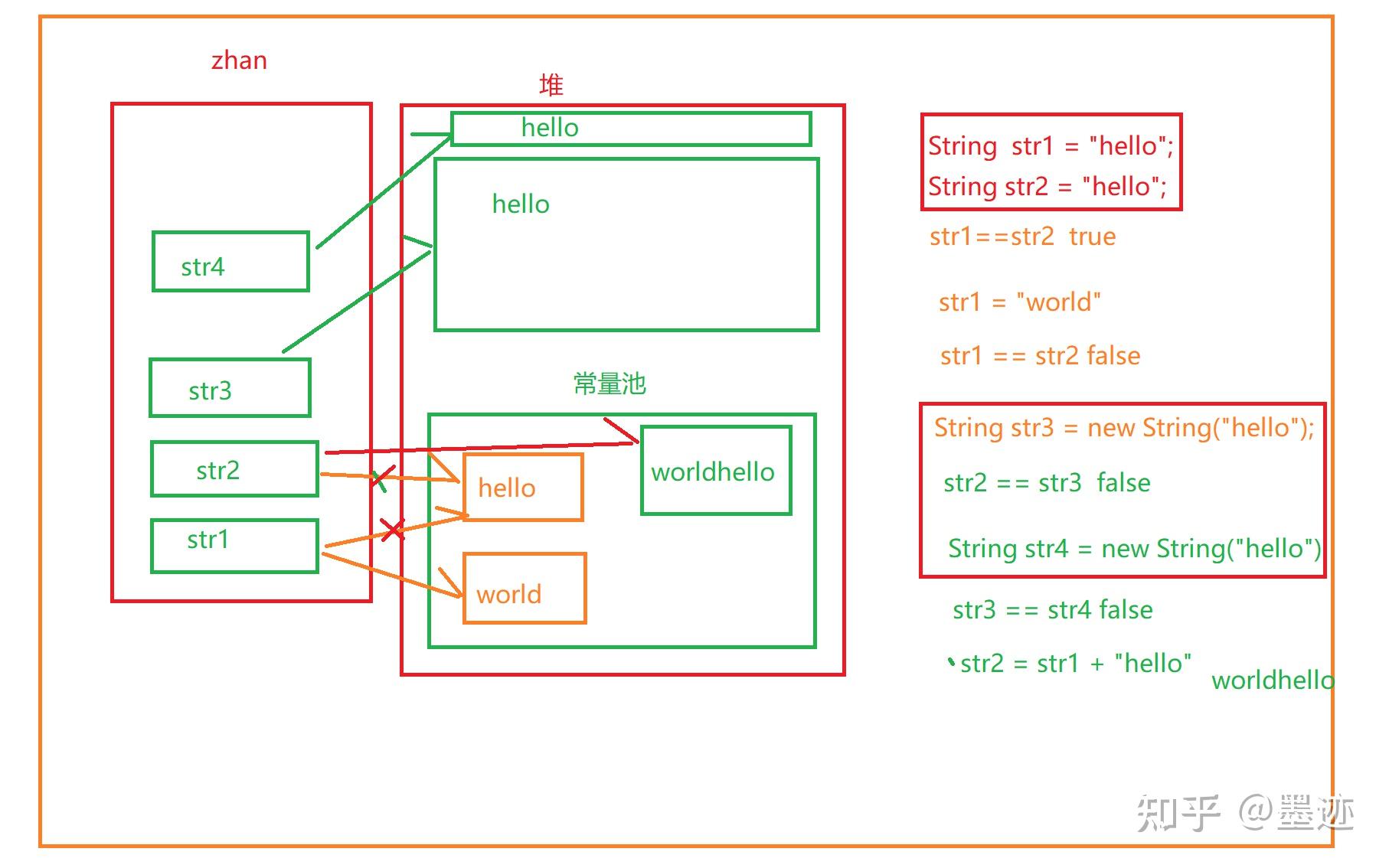
2.1.3关于String的内存分析
String str = "hello";
String str2 = "hello";
String str3 = new String("hello");
worldhello
2.1.4Sting下面的方法
int length(); 返回值是字符串的长度
char charAt(int index); 返回值是指定下标的字符
int indexOf(String str); 返回值是指定字符的下标
int lastIndexOf(int ch); 返回值是指定字符的最后的一个下标
package com.qf.a_string;
public class Demo3 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String str1 = "中国梦";
System.out.println(str1.length());//6
String str2 = "abcdef";
System.out.println(str2.charAt(3));//找str2字符串中下标为 0位置的上的字符
String str3 = "abcdecvf";
System.out.println(str3.indexOf("cd"));//获取的是字符的下标
System.out.println(str3.indexOf(98));//1
System.out.println(str3.indexOf('c'));//2
System.out.println(str3.lastIndexOf('c'));//5
}
}
String toUpperCase(); 返回一个字母全部大写的字符串
String toLowerCase(); 返回一个字母全部小写的字符串
String replace(oldObject, newObject); 返回一个替换过的字符串
String[] split(String str); 以str切割字符串,返回的是一个字符串数组
String subString(int index); 返回值是从指定下标开始截取的字符串 包含指定下标的元素
String subString(int beginIndex,int endIndex); 返回值是截取的指定下标之间的字符串 要头不要尾
String trim(); 去除字符串两边的空格
package com.qf.a_string;
import java.util.Arrays;
public class Demo6 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String str = "abcdef";
System.out.println(str.replace('c', '中'));
System.out.println(str.replace("cd", "牛彩云"));
String str1 = "嘻嘻哒呵呵哒么么哒哈哈哒";
//以哒切割
String[] strs = str1.split("哒");
System.out.println(strs);
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(strs));//[嘻嘻, 呵呵, 么么, 哈哈]
for (int i = 0; i < strs.length; i++) {
System.out.println(strs);
}
String str2 = &#34;ab,cd,ef,g&#34;;
//以, 切割
String[] strs1 = str2.split(&#34;,&#34;);
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(strs1));
//截取一部分的字符串
String str3 = &#34;abcdef&#34;;
System.out.println(str3.substring(2));//cdef
String str4 = &#34;大学先把手机农村&#34;;
System.out.println(str4.substring(2, 4));// 先把//要头不要尾
String str5 = &#34;abCDF&#34;;
System.out.println(str5.toUpperCase());//ABCDF
System.out.println(str5.toLowerCase());//abcdf
String str6 = &#34; index xixi &#34;;
System.out.println(str6);
System.out.println(str6.trim());
}
}String(char[] value, int offset, int count) offset 是偏移量,代表从第几个开始偏移 count是个数
char[] toArray(); 返回值是字符数组 字符串转为字符数组的方法
字符数组转为字符串的方法
1.String str = new String(char[] ch);
2.String str = String.valueOf(char[] ch);
package com.qf.a_string;
public class Demo5 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//将字符数组转为字符串
char[] chs = {&#39;a&#39;, &#39;b&#39;, &#39;c&#39;, &#39;d&#39;, &#39;e&#39;};
String str = new String(chs);
System.out.println(str);//abc
//String(char[] chs, int offset, int count);
//第二个参数 int offset 偏移量 从第几个开始
//第三个参数 int count 个数 数量
String str1 = new String(chs, 4, 1);
System.out.println(str1);
String str2 = String.valueOf(chs);
System.out.println(str2);
//将字符串转为字符数组
char[] arr1 = &#34;狗蛋很狗&#34;.toCharArray();
for (int i = 0; i < arr1.length; i++) {
System.out.println(arr1);
}
}
}
返回值是boolean类型的方法
endWith(String str); 判断当前字符穿是否以所给字符串str结尾
isEmpty(); 判断当前字符串是否为空
contains(String str); 判断当前字符串是否包含所给字符串
equals(String str); 判断当前字符串是否与所给字符相等
equalsIgnoreCase(String str); 判断当前字符串是否与所给字符相等 忽略大小写
package com.qf.a_string;
public class Demo4 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String str1 = &#34;Demo1.java&#34;;
System.out.println(str1.endsWith(&#34;.java&#34;));//true
System.out.println(str1.endsWith(&#34;av&#34;));//false
System.out.println(str1.endsWith(&#34;va&#34;));//true
String str2 = &#34;&#34;;
System.out.println(str2.isEmpty());//true
String str3 = &#34; &#34;;
System.out.println(str3.isEmpty());//flase 不为空 空格也是有内容的
String str4 = &#34;abcdef&#34;;
System.out.println(str4.contains(&#34;cd&#34;));//true
System.out.println(str4.contains(&#34;ce&#34;));//false
System.out.println(str4.contains(&#34;abcde&#34;));//true
System.out.println(str4.equals(&#34;abcdeF&#34;));//false
System.out.println(str4.equalsIgnoreCase(&#34;abcDeF&#34;));//true
}
}2.2泛型
2.2.1为啥要有泛型【重点难点】
广泛的类型
在开发中对数据一致性的要求是比较高的
例如:
数组中存数据 都是同一个类I型的
int[] arr = new int[]
char[] arr = new char[]
通过代码来说明
package com.qf.b_fanxing;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Demo1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] arr = {1,2,3,4};
//STring类不用导包 为啥? 因为 在 java.lang包下面
String[] strs = {&#34;nx&#34;, &#34;hsjj&#34;, &#34;xnjasjn&#34;};
//数组确实可以保证数据类型一致性,但是开发不用!!!为啥? 数组的方法比较少,而且数组容量提前定好的
//不太方便 咋办?学习集合 明天内容
//集合的作用是和数组类似 都是容器 用来存数据的
ArrayList list = new ArrayList();//list 就是容器 就是用来存数据的
list.add(&#34;狗蛋&#34;);//添加
list.add(34);
list.add(&#39;智&#39;);
list.add(true);
System.out.println(list);
//以上代码好不好?不好!!!在开发中对数据一致性的要求是比较高的
//获取一个数据
String obj = (String)list.get(0);
System.out.println(obj);
//需要强转不好,现在有一个技术 泛型 可以保证咱们的数据一致性 针对于集合
//ArrayList<类>
//<String> 告知编译器 此集合只能存放String类型的数据 一致性保证一下
ArrayList<String> list1 = new ArrayList<String>();
list1.add(&#34;张三&#34;);
list1.add(&#34;王二&#34;);
list1.add(&#34;wangliu&#34;);
System.out.println(list1);
String str1 = list1.get(0);
System.out.println(str1);
//泛型在<类> 如果放int类型的数据===》Integer
ArrayList<Integer> list2 = new ArrayList<Integer>();
list2.add(23);
//扩展: 八大基本数据类型所对应的包装类
/**
* byte ==> Byte
* short===>Short
* int===>Integer
* long===>Long
* boolean-===>Boolean
* char===>Character
* float===>Float
* double====>Double
*/
}
}
2.2.2自定义泛型在方法中的应用
语法格式
public <无意的占位符> 返回值类型 方法名(参数){
}无意义的占位符:可以任意的字符 但是都大写的 开发中一般是 T (Type) E (Element) ?(未知)
入门案例
package com.qf.b_fanxing;
public class Demo2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
test(89);// test(T t) T===>Integer
test(&#34;goudan&#34;);// test(T t) T====>String
// public static void test (int i) {
// System.out.println(i);
// }
// public static void test (double i) {
// System.out.println(i);
// }
// public static void test (String i) {
// System.out.println(i);
// }
}
//写泛型的入门级别的案例 更具有广泛性质
//T随着方法的实参 而改变他的类型
public static <T> void test(T t) {//T 代表所有的类型
System.out.println(t);
}
}
无参无返回值
有参无返回值
无参有返回值
有参有返回值
无参的话泛型就无意义了,通过代码解释
package com.qf.b_fanxing;
public class Demo3 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
test();
}
//无参无返回值的方法 没有必要使用泛型
public static <T> void test () {
System.out.println(&#34;hewllo world&#34;);
}
//有参无返回值的方法 可以使用
public static <T> void test (T t, T t1) {
//t 是多个类型 操作的时候要符合数据类型相对应的操作方式
System.out.println(t + &#34;&#34; + t1);
}
//无参 有返回值的 没有必要使用泛型的
public static <T> T test1 () {
return null;
}
//有参 有返回值的方fa 写起来有局限性
public static <T> T test2 (T t, T t1) {
return t;
}
//有参的才有一点用途
}
2.2.3泛型类【重点】
语法格式
class 类名<无意义的占位符>{
}
package com.qf.b_fanxing;
class Person<T> {
//泛型类中可以有普通的方法
public void eat() {
System.out.println(&#34;吃饭饭&#34;);
}
//带有泛型的方法
//public <T> void test() {一般在泛型类中的方法中不要去写<T> 因为方法的参数 根据类后面的<T> 来约束的
public void test (T t) {
System.out.println(t);
}
//静态方法 自娱自乐
//当创建对象的时候才确定泛型类型,静态方法早于对象的创建,所以你的泛型对我是没有任何用的
//告知程序员此处的泛型和类的泛型没有关系的
public static <E> void test1 (E e) {
System.out.println(e);
}
}
public class Demo4 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Person.test1(78);
Person<String> strPerson = new Person<String>();
//现在T是String 就意味者在调用test方法的时候 参数只能传String
strPerson.test(&#34;goudan&#34;);
//strPerson.test(89);
}
}
2.2.4泛型抽象类
语法格式
abstract class 类名<无意义的占位符>(参数){
}
package com.qf.b_fanxing;
abstract class A<T> {
abstract void test(T t);
}
//1.在继承抽象类时候 子类也必须带有和父类相同的泛型占位符
class ATest<T> extends A<T> {
void test(T t) {
}
}
public class Demo5 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ATest<Integer> aTest = new ATest();
aTest.test(67);
}
}
2.2.5泛型接口
语法格式
interface 接口名<无意义的占位符>{
}3.day17
3.1权限修饰符
| 可以在本类中使用 | 可以在当前包使用 | 可以在其他包的子类使用 | 可以在其他包使用(在本项目内) | | private | √ | × | × | × | | 默认的 | √ | √ | × | × | | protected | √ | √ | √ | × | | public | √ | √ | √ | √ |
3.2集合
3.2.1为啥要有集合
集合和数组都是可以存数据的
真实开发的时候用的是集合而不是数组
为啥?
1.数组的容量是固定的。
2.数组封装的方法比较少。
Java给咱们封装了集合类库,只需要实例化出来一个对象,使用对象调用方法即可完成数据相关的操作
3.2.2集合结构
Interface Collection<E> Java 中集合的总接口
当前只学Collection
ArrayList底层是数组,LinkedList底层是链表,Vector暂时不学,先知道就行
HashSet底层是Hash算法,TreeSet底层是二叉树
3.2.3Collection接口【开发不用】
先看Collectiom接口下面的方法
//返回值类型
增
boolean add(E e); 添加指定元素到集合里
boolean addAll(Collection<? extends e> c); 添加指定集合到集合里
删
boolean remove(E e); 删除集合里的指定元素
boolean remove(Collection<? extends e> c); 删除指定集合
void clear(); 清空集合
查
boolean isEmpty(); 判断集合是否为空
boolean contains(E e); 判断是否包含指定元素
boolean contains(Collection<? extends e> c); 判断是否包含指定集合
Object[] toArray(); 集合转为数组
int size(); 集合中元素的个数
package com.qf.c_collection;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Collection;
public class Demo1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//父类的引用指向了子类的对象,意味着 对象只能调用父类的方法
//对象不能调用子类独有的方法 只能调用重写的方法
//Collection 所有的抽象方法都被ArrayList 重写了
Collection<String> collection = new ArrayList<String>();//容器 只能放String类型的数据
collection.add(&#34;红旗渠&#34;);
collection.add(&#34;散花&#34;);
collection.add(&#34;黄鹤楼&#34;);
System.out.println(collection);//[红旗渠, 散花, 黄鹤楼]
Collection<String> collection1 = new ArrayList<String>();//容器 只能放String类型的数据
collection1.add(&#34;舍得&#34;);
collection1.add(&#34;茅台&#34;);
collection1.add(&#34;牛栏山&#34;);
System.out.println(collection1);
collection.addAll(collection1);//将collection1这个集合添加到collection中
System.out.println(collection);//[红旗渠, 散花, 黄鹤楼, 舍得, 茅台, 牛栏山]
// Collection<Integer> collection2 = new ArrayList<Integer>();//容器 只能放String类型的数据
// collection2.add(1);
// collection2.add(2);
// collection2.add(3);
//
// collection.addAll(collection2);
System.out.println(collection.remove(&#34;舍得&#34;));//删除指定的数据
System.out.println(collection);//删除之后的结果
//[红旗渠, 散花, 黄鹤楼, 茅台, 牛栏山]
//System.out.println(collection.remove(&#34;舍得&#34;));
Collection<String> collection3 = new ArrayList<String>();//容器 只能放String类型的数据
collection3.add(&#34;舍得&#34;);
collection3.add(&#34;茅台&#34;);
collection3.add(&#34;牛栏山&#34;);
collection3.add(&#34;红花郎&#34;);
System.out.println(collection3);//[舍得, 茅台, 牛栏山, 红花郎]
collection.removeAll(collection3);//删除指定集合中包含的所有此集合的元素
//在collection 删除collection3 中包含的元素
System.out.println(collection);//[红旗渠, 散花, 黄鹤楼]
collection.clear();
System.out.println(collection);//[]
}
}
3.2.4遍历集合中的数据
三种方法:for循环,增强for循环,迭代器
3.2.4.1for循环
语法格式
for(语句体1,布尔表达式,语句体2){
循环体
}package com.qf.c_collection;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Collection;
public class Demo2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Collection<Character> list = new ArrayList<Character>();
list.add(&#39;a&#39;);
list.add(&#39;b&#39;);
list.add(&#39;c&#39;);
System.out.println(list);//[a, b, c]
//for循环遍历
//将集合转为数组 然后再遍历
Object[] objs = list.toArray();
for (int i = 0; i < objs.length; i++) {
System.out.println(objs);
}
}
}
3.2.4.2增强for循环
语法格式
for(集合或数组元素的数据类型 临时变量名:集合或者数组){
语句体
}
package com.qf.c_collection;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Collection;
public class Demo3 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Collection<String> liStrings = new ArrayList<String>();
liStrings.add(&#34;张三&#34;);
liStrings.add(&#34;狗蛋&#34;);
liStrings.add(&#34;老邢&#34;);
System.out.println(liStrings);
//使用增强for循环遍历数据
for (String s : liStrings) {
System.out.println(s);
}
}
}
3.2.4.3迭代器
语法格式
Iterator<E> iterator = 集合名.Iterator<E>();//声明一个迭代器
while(iterator.hasNext){//判断游标后一位是否有数据,从前往后 hasPrevious是从后往前(两张方法游标的起始位置都在第一个要遍历的的元素之前)
iterator.next//返回游标后一位元素并将游标向后移动一位 previous
}
package com.qf.c_collection;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Collection;
import java.util.Iterator;
public class Demo4 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Collection<String> liStrings = new ArrayList<String>();
liStrings.add(&#34;张三&#34;);
liStrings.add(&#34;狗蛋&#34;);
liStrings.add(&#34;老邢&#34;);
//使用迭代器进行遍历
// Iterator<E> iterator() 是Collection 方法
// 返回此集合中的元素的迭代器。
//将集合变成了一个迭代器对象 这个迭代器有没有数据? 有集合中原始的数据的
//1.创建迭代器的对象
Iterator<String> iterator = liStrings.iterator();
//boolean hasNext()如果迭代具有更多元素,则返回 true 。
// [&#34;张三&#34;, &#34;狗蛋&#34;, &#34;老邢&#34;]
// ||
//游标
// System.out.println(iterator.hasNext());//判断游标后面有没有元素 true
// System.out.println(iterator.next());//返回迭代的下一个元素,并将游标往后挪一位
// System.out.println(iterator.hasNext());
// System.out.println(iterator.next());//狗蛋
// System.out.println(iterator.hasNext());//true
// System.out.println(iterator.next());//老邢
// System.out.println(iterator.hasNext());//false
// System.out.println(iterator.next());
while (iterator.hasNext()) {
System.out.println(iterator.next());
}
}
}
3.2.5List接口
Collection父接口
开发中使用List 而不是Collection 为啥呢?
List下面有自己独有的一些方法,子接口比父接口的功能全
子接口不但重写父接口所有的方法而且加了自己的独有方法
所以开发用List
List存储数据是有序且可重复的
List独有的方法
增
boolean add(int index); 在指定下标的位置增加元素
boolean add(int index,Collection<? extends E> c); 在指定下标的位置增加集合
删
boolean remove(int index); 删除指定下标的元素
改
E set(int index,E e); 更改指定下标的元素,返回值是被更改的元素
取
E get(int index); 获得指定下标的元素
E indexOf(Object objec); 获得指定元素的下标
E LastIndexOf(Object objec); 获取指元素的最后一个位置
List<E> subList(int startIndex,int endIndex); 截取指定下标的集合,要头不要尾
package com.qf.d_list;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
public class Demo1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
List<String> list = new ArrayList<String>();
System.out.println(list);
list.add(&#34;狗蛋&#34;);
list.add(&#34;张三&#34;);
list.add(&#34;李四&#34;);
list.add(&#34;张三&#34;);
list.add(&#34;李四&#34;);
list.add(&#34;李四&#34;);
list.add(&#34;张三&#34;);
System.out.println(list);//[狗蛋, 张三, 李四]
list.add(1, &#34;王五&#34;);//在指定的下标的位置上面添加一个元素
System.out.println(list);//[狗蛋, 王五, 张三, 李四]
//通过元素删除
System.out.println(list.remove(&#34;二蛋&#34;));//false
//通过索引下标删除
System.out.println(list.remove(0));//狗蛋
//
System.out.println(list);//被删除之后的集合元素
//[王五, 张三, 李四]
System.out.println(list.set(1, &#34;王八&#34;));//返回值是被替换的元素
System.out.println(list);//[王五, 王八, 李四]
System.out.println(list.get(2));//李四
System.out.println(list.indexOf(&#34;王博&#34;));//-1
System.out.println(list.indexOf(&#34;王八&#34;));//1
System.out.println(list.lastIndexOf(&#34;张三&#34;));//6
//list = [王五, 王八, 李四, 张三, 李四, 李四, 张三]
System.out.println(list.subList(2, 4));//[李四, 张三]
}
}
3.2.6List接口遍历数据
for循环
package com.qf.d_list;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
public class Demo2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
List<String> list = new ArrayList<String>();
list.add(&#34;狗蛋&#34;);
list.add(&#34;张三&#34;);
list.add(&#34;李四&#34;);
list.add(&#34;张三&#34;);
list.add(&#34;李四&#34;);
list.add(&#34;李四&#34;);
list.add(&#34;张三&#34;);
System.out.println(list);//[狗蛋, 张三, 李四]
for (int i = 0; i < list.size(); i++) {
System.out.println(list.get(i));
}
}
}增强for循环
package com.qf.d_list;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
public class Demo3 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
List<String> list = new ArrayList<String>();
list.add(&#34;狗蛋&#34;);
list.add(&#34;张三&#34;);
list.add(&#34;李四&#34;);
list.add(&#34;张三&#34;);
list.add(&#34;李四&#34;);
list.add(&#34;李四&#34;);
list.add(&#34;张三&#34;);
for (String string : list) {
System.out.println(string);
}
}
}
迭代器
package com.qf.d_list;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.ListIterator;
public class Demo4 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
List<String> list = new ArrayList<String>();
list.add(&#34;狗蛋&#34;);
list.add(&#34;张三&#34;);
list.add(&#34;李四&#34;);
list.add(&#34;张三&#34;);
list.add(&#34;李四&#34;);
list.add(&#34;李四&#34;);
list.add(&#34;张三&#34;);
// ListIterator<String> listIterator = list.listIterator();
// while (listIterator.hasNext()) {
// System.out.println(listIterator.next());
// }
// //循环结束代码走到这一步 咱们的光标在 最后一个位置
// System.out.println(&#34;=========&#34;);
// //上一个是否有元素
// while (listIterator.hasPrevious()) {
// //返回上一个元素并且 光标向上一个
// System.out.println(listIterator.previous());
// }
ListIterator<String> listIterator = list.listIterator(list.size());
while (listIterator.hasPrevious()) {
System.out.println(listIterator.previous());
}
}
} |
|